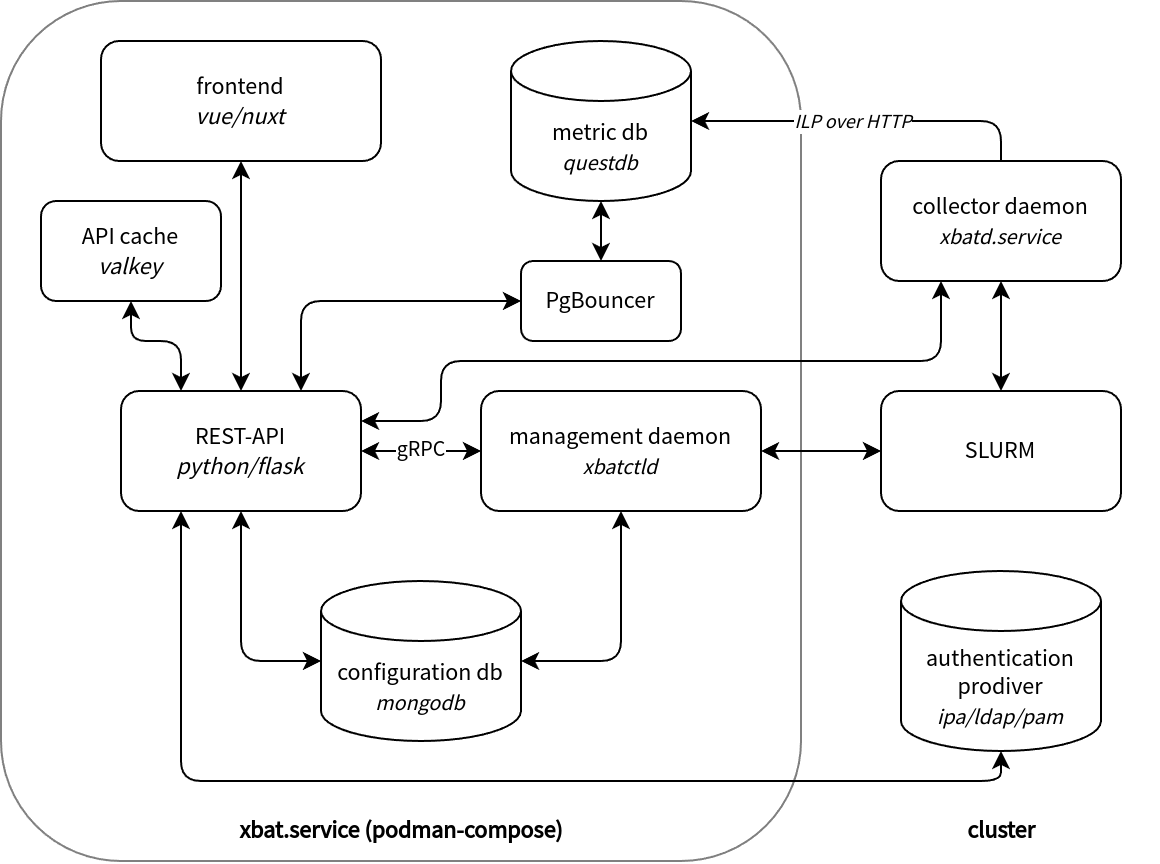
The architecture is composed of several components that work together to provide a comprehensive benchmarking solution. Below is an overview of the key components and their interactions. To provide seamless integration into existing HPC infrastructures, xbat leverages a docker/podman-compose infrastructure and connects to various systems already present on the cluster.
The workflows for jobs submitted through the user interface and the CLI differ, but ultimately converge once a job is submitted.
When a user submits a benchmark via the user interface, the REST-API backend forwards all relevant information via gRPC to the management daemon (xbatctld). This daemon registers the benchmark in the database, generates the corresponding job script, and places it in the user's home directory under .xbat/scripts. The job is then submitted to the batch system on behalf of the user, which schedules it for execution on the cluster. During this process, xbatctld continuously monitors the Slurm queue and updates all job-related data in the database, including job output, job state, and more.
As soon as a job is scheduled by Slurm, the workflows for the user interface and CLI converge. When job execution begins, a Slurm Prolog script is triggered, which starts the collector daemon (xbatd.service). Upon starting, xbatd authenticates with the REST-API, registers the job in the database, and retrieves additional instructions (e.g., settings). If no information about the node's hardware, software, or performance capabilities is stored in the database, the daemon collects this data and forwards it to the REST-API. Identical nodes are not re-examined, as the node data is hashed; nodes with identical hashes are automatically skipped.
After this initialization phase, xbatd continuously collects performance data and writes it to the QuestDB database using the Influx Line Protocol over HTTP. The necessary tables are created automatically if they do not already exist. At the end of the job, the Slurm Epilog script stops the daemons, concluding the workflow.
For seamless integration into existing clusters, xbat is able to connect to either IPA, LDAP or PAM for authentication. On every login, the user's credentials are verified against the configured authentication provider. If the user does not exist in the database, they are automatically created with default permissions. See the User Management Guide for more details.